编者注:我们发现了有趣的系列文章《30天学习30种新技术》,正在翻译,一天一篇更新,年终礼包。下面是第 30 天的内容。
今天是最后一天,我决定学习一下 Play 框架。原本是想写关于Scala的,学习了几个小时之后发现在一天之内是不可能完成Scala的,所以今天会介绍一下Play框架的基本知识,然后学习如何用它开发应用。

什么是 Play 框架?
Play是一个开源的现代web框架,用于编写Java和Scala的可扩展Web应用程序。它通过自动重载变化来提高生产力,由于设计的就是一个无状态、无阻塞的架构,所以用Play框架来编写横向扩展Web应用程序是很容易的。
为什么要用它?
我的原因是:
开发人员生产力:我已经写了8年的Java,但在过去的几个月里我把更多的时间花在了Python和JavaScript (Node.js) 上。用动态语言工作时最让我吃惊的,就是用它编写程序的速度是如此之快。Java EE和Spring框架并不是快速原型和开发的理想选择,但在用Play框架时,你更改一处刷新一下页面,更新会立即出现,而且它支持热重载所有的Java代码、模板等,可以让你的迭代快很多。
天性使然:Play框架是建立在Netty之上的,所以它支持非阻塞I/O,这使得并行远程调用容易了很多,这一点对面向服务的架构中的高性能应用程序是很重要的。
支持Java和Scala:Play框架是一个真正的多语种Web框架,开发者可以在项目中同时使用Java和Scala。
一流的REST JSON支持:它很容易编写基于REST的应用。对HTTP路由有很好的支持,HTTP路由会将HTTP请求转化为具体动作;JSON编组/解组API是目前的核心API,所以没有必要加一个库来做到这一点。
应用类型案例
今天的介绍中,将开发一个社交书签应用程序,它允许用户发布和共享链接。你可以在这里查看正在运行的该程序,因为这个和第22天的应用是一样的,所以请参阅之以便更好地了解这个案例。
开发Play应用
请参阅文档以了解如何安装Play框架,开始应用程序的开发吧。
$ play new getbookmarks
_
_ __ | | __ _ _ _
| '_ \| |/ _' | || |
| __/|_|\____|\__ /
|_| |__/
play 2.2.1 built with Scala 2.10.2 (running Java 1.7.0_25), http://www.playframework.com
The new application will be created in /Users/shekhargulati/dev/challenges/30days30technologies/day30/blog/getbookmarks
What is the application name? [getbookmarks]
>
Which template do you want to use for this new application?
1 - Create a simple Scala application
2 - Create a simple Java application
> 2
OK, application getbookmarks is created.
Have fun!
如上键入命令后,该框架会问几个问题。首先它要求有应用程序的名称,然后问是否要创建一个Scala或Java应用程序。默认情况下,它会使用文件夹名称作为应用程序的名称。
上面的命令将创建一个新的目录getbookmarks并生成以下文件和目录:
- app 目录包含如控制器 (controller) 、视图 (view) 和模型 (model) 的应用程序特定代码。控制器包中有响应URL路由的Java代码,视图目录包含服务器端模板,模型目录包含应用程序的域模型。在此应用中,域 (domain) 是一个Story类。
- conf 目录包含应用程序配置和路由定义文件。
- project 目录包含构建脚本,构建系统是基于SBT的。
- public 包含了如CSS、JavaScript和img目录等的公共资源。
- test 目录包含应用测试。
通过如下命令发布play控制台,运行Play编写的默认程序。
$ cd getbookmarks
$ play
[info] Loading project definition from /Users/shekhargulati/dev/challenges/30days30technologies/day30/blog/getbookmarks/project
[info] Set current project to getbookmarks (in build file:/Users/shekhargulati/dev/challenges/30days30technologies/day30/blog/getbookmarks/)
_
_ __ | | __ _ _ _
| '_ \| |/ _' | || |
| __/|_|\____|\__ /
|_| |__/
play 2.2.1 built with Scala 2.10.2 (running Java 1.7.0_25), http://www.playframework.com
> Type "help play" or "license" for more information.
> Type "exit" or use Ctrl+D to leave this console.
[getbookmarks] $ run
[info] Updating {file:/Users/shekhargulati/dev/challenges/30days30technologies/day30/blog/getbookmarks/}getbookmarks...
[info] Resolving org.fusesource.jansi#jansi;1.4 ...
[info] Done updating.
--- (Running the application from SBT, auto-reloading is enabled) ---
[info] play - Listening for HTTP on /0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:9000
(Server started, use Ctrl+D to stop and go back to the console...)
现在可以在 http://localhost:9000 里运行该应用了。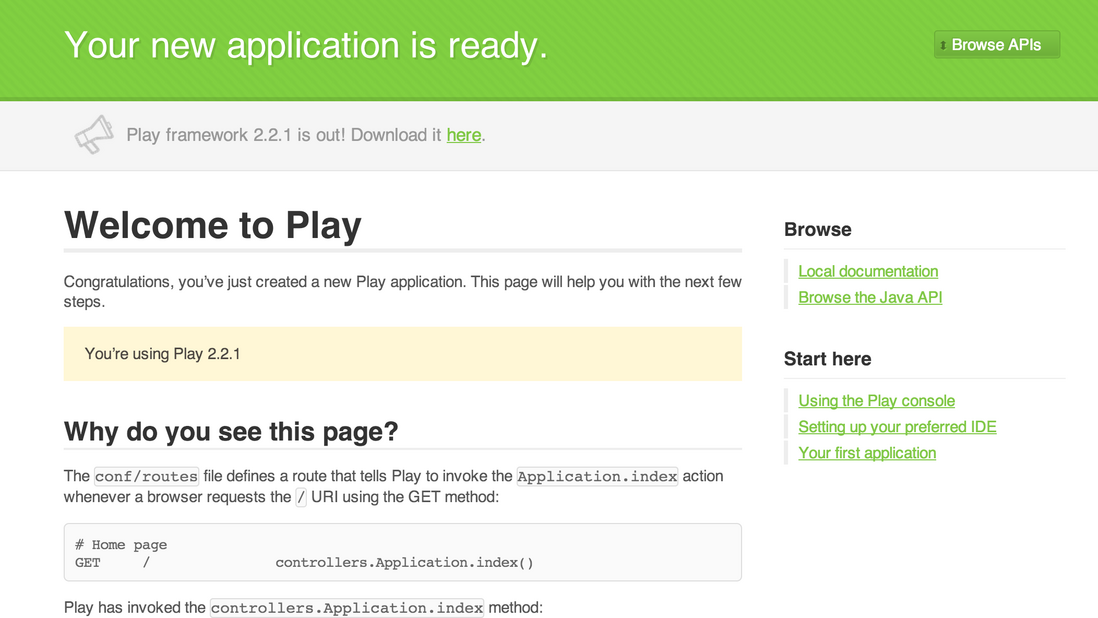
创建Story域类
该应用程序只有一个域类 (domain class),叫做story,创建一个新的包模型和Java类。
package models;
import play.db.ebean.Model;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import java.util.Date;
@Entity
public class Story extends Model{
@Id
private String id;
private String url;
private String fullname;
private Date submittedOn = new Date();
private String title;
private String text;
private String image;
public Story() {
}
public Story(String url, String fullname) {
this.url = url;
this.fullname = fullname;
}
public Story(String url, String fullname, String image, String text, String title) {
this.url = url;
this.fullname = fullname;
this.title = title;
this.text = text;
this.image = image;
}
// Getter and Setter removed for brevity
}
上述代码定义了一个简单的JPA实体,并使用 @Entity 和 @Id JPA注解,Play用它自己的一个被称作Ebean的ORM层,而且每一个实体类必须扩展基本模型类。
Ebean默认禁用,启用它需要打开application.conf并取消注释以下行。
ebean.default="models.*"
启用数据库
启动应用程序的数据库,Play框架提供了内置的H2数据库的支持。要启用它,打开application.conf文件,并取消如下两行的注释。
db.default.driver=org.h2.Driver
db.default.url="jdbc:h2:mem:play"
刷新浏览器会看到: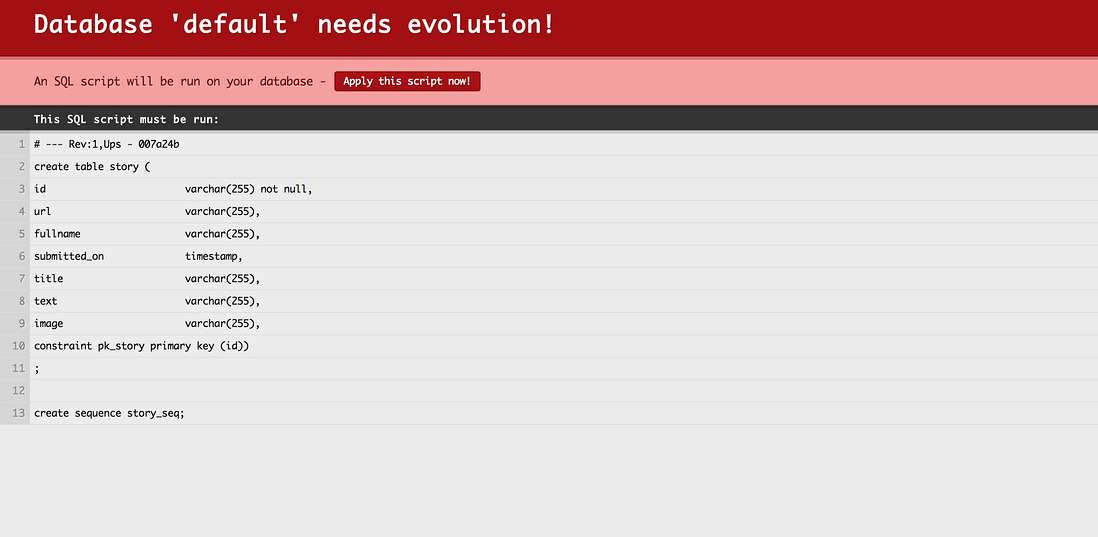
点击Apply this script now将SQL的更改部署上去。
定义应用程序的路由
今天讲的应用程序和第22天是一样的,都有AngularJS后台和REST后端,所以可以使用Play框架重写REST后台和AngularJS后端,在conf/routes文件,复制并粘贴如下代码。
# Routes
# This file defines all application routes (Higher priority routes first)
# ~~~~
# Home page
GET / controllers.Assets.at(path="/public", file="/index.html")
GET /api/v1/stories controllers.StoryController.allStories()
POST /api/v1/stories controllers.StoryController.submitStory()
GET /api/v1/stories/:storyId controllers.StoryController.getStory(storyId)
# Map static resources from the /public folder to the /assets URL path
GET /assets/*file controllers.Assets.at(path="/public", file)
上述代码表示:
- 当用户发出一个GET请求到应用程序的
“/”URL,index.html将被渲染。 - 当用户发出一个GET请求到
'/ api/v1/stories',将得到JSON格式的所有story。 - 当用户发出POST请求到
'/ api/v1/stories',一个新的story将被创建。 - 当用户GET请求
'/ api/v1/stories/123',id为123的story会被渲染。
创建Story控制器
在控制器包里创建一个Java类,将如下代码粘贴进 StoryController.java 文件里。
package controllers;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import models.Story;
import play.api.libs.ws.Response;
import play.api.libs.ws.WS;
import play.db.ebean.Model;
import play.libs.Json;
import play.mvc.BodyParser;
import play.mvc.Controller;
import play.mvc.Result;
import play.mvc.Results;
import scala.concurrent.Await;
import scala.concurrent.Future;
import scala.concurrent.duration.Duration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class StoryController {
public static Result allStories(){
List<Story> stories = new Model.Finder<String , Story>(String.class, Story.class).all();
return Results.ok(Json.toJson(stories));
}
@BodyParser.Of(BodyParser.Json.class)
public static Result submitStory(){
JsonNode jsonNode = Controller.request().body().asJson();
String url = jsonNode.findPath("url").asText();
String fullname = jsonNode.findPath("fullname").asText();
JsonNode response = fetchInformation(url);
Story story = null;
if(response == null){
story = new Story(url,fullname);
}else{
String image = response.findPath("image").textValue();
String text = response.findPath("text").textValue();
String title = response.findPath("title").textValue();
story = new Story(url,fullname, image , text , title);
}
story.save();
return Results.created();
}
public static Result getStory(String storyId){
Story story = new Model.Finder<String, Story>(String.class, Story.class).byId(storyId);
if(story == null){
return Results.notFound("No story found with storyId " + storyId);
}
return Results.ok(Json.toJson(story));
}
private static JsonNode fetchInformation(String url){
String restServiceUrl = "http://gooseextractor-t20.rhcloud.com/api/v1/extract?url="+url;
Future<Response> future = WS.url(restServiceUrl).get();
try {
Response result = Await.result(future, Duration.apply(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
JsonNode jsonNode = Json.parse(result.json().toString());
return jsonNode;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
上述代码会操作:
它定义
allStories()方法,该方法会找到数据库中所有的story。它是使用Model.Finder API来做到这一点的,然后把story列表转换成JSON格式并返回结果,返回HTTP状态代码200(即确定)。submitStory()方法首先会从JSON读取URL和全名的字段,然后发送GET请求到'http://gooseextractor-t20.rhcloud.com/api/v1/extract?url',这样就会找出标题、摘要以及已经给定url的主要image。创建一个使用所有信息的story并保存在数据库中,返回HTTP状态代码201(即创建)。getStory()方法为给定的storyId获取story,把这个story转换成JSON格式并返回响应。
可以从我的github仓库下载AngularJS前端,用其中一个库更换公共目录。
现在可以访问http://localhost:9000/看结果了。
30天系列的文章就此结束,非常感谢大家的持续关注,也希望你们能和SegmentFault一块成长。
So, see you next year. Oh~ Happy New Year to Y'all !
原文 Day 30: Play Framework--A Java Developer Dream Framework
翻译整理 SegmentFault
